| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
Tags
- 컨디션 변수
- 병행성
- 알고리즘
- 그리디 알고리즘
- codility
- directx
- 렌더링 파이프라인
- 병행성 관련 오류
- OS
- Direct12
- 동적계획법
- 다이나믹프로그래밍
- 디자인패턴
- DirectX12
- 쓰레드
- 멀티쓰레드
- 타입 객체
- DirectX 12
- I/O장치
- 그리디알고리즘
- 프로그래머스
- 스케줄링
- 운영체제
- 락
- 백준
- 영속성
- 자료구조
- 다이나믹 프로그래밍
- 멀티프로세서
- 파일시스템 구현
Archives
- Today
- Total
기록공간
유기농 배추 (백준) 본문
반응형
DFS, BFS를 잘 알고 있다면 어렵지 않은 문제였다.
너비 우선 탐색 (BFS)
너비 우선 탐색 (Breadth Firest Search : BFS)은 그래프의 모든 정점들을 특정한 순서에 따라 방문하는 알고리즘 중 하나이다. 현재 정점과 인접한 모든 간선을 우선적으로 검사하며, 그 중 방문하지 ��
lipcoder.tistory.com
깊이 우선 탐색 (DFS)
깊이 우선 탐색 (Depth First Search : DFS)은 그래프의 모든 정점들을 특정한 순서에 따라 방문하는 알고리즘 중 하나이다. 현재 정점과 인접한 간선들을 검사하다가 방문하지 않은 정점을 발견하면 ��
lipcoder.tistory.com
DFS, BFS 둘 중 무엇을 사용하더라도 정답이 도출되기 때문에 더 잘되는 것을 사용하면 된다.
배추 지렁이는 상하좌우로 갈 수 있으며 인접한 배추가 없을때까지 갈 수 있다. 배추가 배치되어 있는 영역의 갯수를 안다면 지렁이를 몇 개 배치해야 하는지를 알 수 있다.
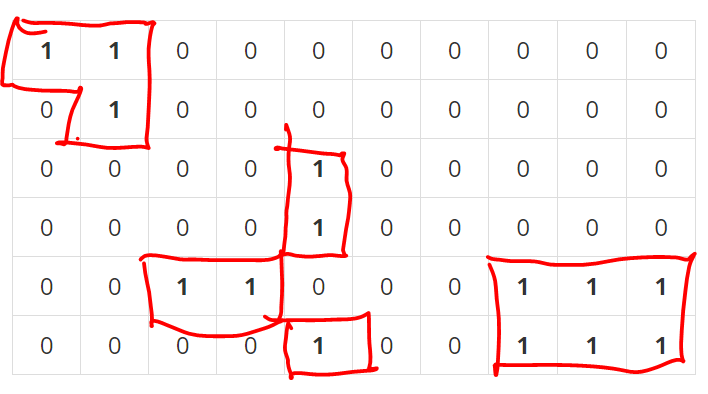
위 예제 같은 경우 배추의 영역이 총 5개가 있으므로 배추 지렁이는 최소 5마리가 필요하다. 이 영역을 DFS, BFS를 이용하여 구해주면 된다.
이미 방문한 곳을 또 방문하지 않도록 하기 위해 방문한 곳을 체크해주는 데이터를 담은 컨테이너가 필요하다. 방문할때마다 이 컨테이너에 기록한다.
코드는 다음과 같다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
// 깊이탐색
void dfs(vector<vector<bool>>& c, vector<vector<int>>& soil, int x, int y)
{
int limit_x = soil[0].size(), limit_y = soil.size();
stack<vector<int>> s;
s.push({ y, x });
while (!s.empty())
{
vector<int> pos = s.top();
int push_check = s.size();
// 하, 상, 좌, 우 순으로 갈 수 있는 방향으로 먼저 간다.
if (pos[0] - 1 >= 0 && soil[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]] == 1 && !c[pos[0] - 1][pos[1]])
s.push({ pos[0] - 1, pos[1] });
else if (pos[0] + 1 < limit_y && soil[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]] == 1 && !c[pos[0] + 1][pos[1]])
s.push({ pos[0] + 1, pos[1] });
else if (pos[1] - 1 >= 0 && soil[pos[0]][pos[1] - 1] == 1 && !c[pos[0]][pos[1] - 1])
s.push({ pos[0], pos[1] - 1 });
else if (pos[1] + 1 < limit_x && soil[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1] == 1 && !c[pos[0]][pos[1] + 1])
s.push({ pos[0], pos[1] + 1 });
// 앞으로 나아갈 수 없는 경우
// 이전위치로 돌아가기 위해 pop한다.
if (push_check == s.size()) s.pop();
// 방문 체크
c[pos[0]][pos[1]] = true;
}
}
// 너비탐색
void bfs(vector<vector<bool>>& c, vector<vector<int>>& soil, int x, int y)
{
int limit_x = soil[0].size(), limit_y = soil.size();
int result = 0;
queue<vector<int>> q;
q.push({ y + 1, x }); q.push({ y - 1, x });
q.push({ y, x + 1 }); q.push({ y, x - 1 });
while (!q.empty())
{
vector<int> pos = q.front();
q.pop();
// 범위를 벗어난 경우
if (pos[0] < 0 || pos[0] >= limit_y) continue;
if (pos[1] < 0 || pos[1] >= limit_x) continue;
// 이미 방문했거나, 배추가 있는 위치가 아닌경우
if (soil[pos[0]][pos[1]] == 0 || c[pos[0]][pos[1]]) continue;
q.push({ pos[0] + 1, pos[1] }); q.push({ pos[0] - 1, pos[1] });
q.push({ pos[0], pos[1] + 1 }); q.push({ pos[0], pos[1] - 1 });
c[pos[0]][pos[1]] = true;
}
}
int main()
{
int test_case;
cin >> test_case;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> soil(test_case);
vector<int> result;
for (int i = 0; i < test_case; ++i)
{
int x, y, v;
cin >> x >> y >> v;
soil[i].assign(y, vector<int>(x, 0));
for (int j = 0; j < v; ++j)
{
int v_x, v_y;
cin >> v_x >> v_y;
soil[i][v_y][v_x] = 1;
}
}
for (int k = 0; k < test_case; ++k)
{
// 방문 체크를 위한 컨테이너 생성
vector<vector<bool>> check(soil[k].size(), vector<bool>(soil[k][0].size(), false));
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < soil[k].size(); ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < soil[k][0].size(); ++j)
{
// 배추 밭이고 방문 한 적이 없는 위치인 경우
if (soil[k][i][j] == 1 && !check[i][j])
{
// 그 위치에서부터 탐색 시작
bfs(check, soil[k], j, i);
// dfs(check, soil[k], j, i);
++count;
}
}
}
result.push_back(count);
}
for (const auto r : result) cout << r << endl;
return 0;
}
반응형
'Algorithm > 문제' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 타겟넘버 (프로그래머스) (0) | 2020.07.01 |
|---|---|
| 강의실 배정 (백준) (0) | 2020.06.22 |
| 궁금한 민호 (백준) (0) | 2020.06.19 |
| 보석 도둑 (백준) (0) | 2020.06.19 |
| 섬 연결하기 (프로그래머스) (2) | 2020.06.18 |
Comments




